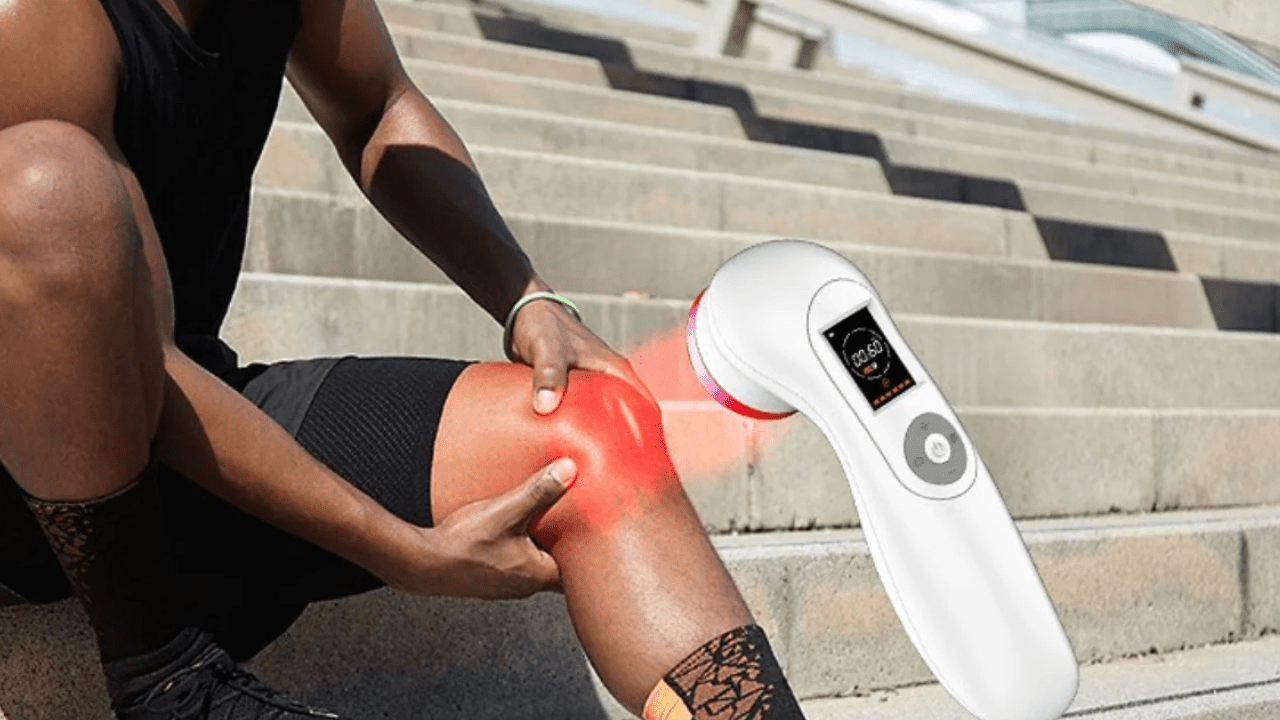
How Is Cold Laser Therapy Based On Science?
Because cold laser therapy promotes healing and reduces a variety of ailments in a non-invasive, safe, and effective manner, it is used. Its capacity to increase cellular activity through photobiomodulation the process of using particular light wavelengths to interact with cellular components without producing heat is one of the main reasons for its use. This procedure speeds up tissue repair, increases ATP synthesis, and improves cellular metabolism.
Applications of cold laser therapy are in high demand in a variety of medical specialties, such as neurology, musculoskeletal disorders, wound healing, and pain management. Its few side effects add to its appeal, and its non-invasive nature makes it a favorite choice for people looking for alternatives to surgery or drugs. Cold laser treatment provides a flexible and promising means see this page for treating everything from chronic pain to speeding up the healing process after injuries.
Cold Laser Therapy Based On Science
We investigate the molecular principles that underpin the effectiveness of cold laser therapy, delving into the complex science behind this treatment.
Photobiomodulation
Photobiomodulation, the idea that light interacts with biological tissues to cause cellular responses, is central to cold laser therapy. This interaction happens when cellular chromophores, mainly mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase, absorb photons from the laser or LED light.
Mitochondrial Activation
Often referred to as the cell’s powerhouse, the mitochondria are essential for energy production and cellular metabolism. Cytochrome c oxidase undergoes a photochemical process in response to certain light wavelengths, which raises cellular respiration and produces adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This increase in ATP is crucial for providing energy to cells and supporting various cellular functions.
Wavelength Selection
Choosing the right wavelengths is essential to the efficacy of cold laser therapy. From red (about 630–680 nm) to near-infrared (approximately 800-1000 nm) are often used wavelengths. These wavelengths are selected to ensure the best possible treatment results because of their capacity to enter tissues and interact with cellular constituents.
Impact on Cellular Redox State
Research has demonstrated that cold laser therapy alters the cellular redox state, which in turn affects how well oxidants and antioxidants are balanced inside of cells. The regulation of cellular functions and the mitigation due to oxidative stress are contingent upon this modulation. Cold laser therapy supports a more favorable redox environment, which enhances cellular resilience and health.
Diminished Inflammatory Mediators
Pro-inflammatory cytokines are among the many mediators involved in the intricate biological reaction known as inflammation. It has been shown that cold laser therapy can lower the expression and activity of certain inflammatory mediators, such as interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α). Treating illnesses linked to chronic inflammation requires this anti-inflammatory action.
Mitigation of Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress is a situation marked by an imbalance between the creation of oxygen species that respond (ROS) and the cell’s ability to neutralize them. One way to mitigate oxidative stress is by the use of cold laser treatment. Cold laser therapy promotes overall cellular health and helps prevent oxidative stress-related cellular damage by regulating ROS levels.
Immunomodulation
The immune system is influenced by cold laser therapy, which modifies immune cell function. According to studies, the treatment may improve macrophage phagocytic activity, which would aid in the removal of cellular waste and support a balanced immune response. Inflammatory and immune-related disorders benefit greatly from this immunomodulatory action.
Vasodilation and Enhanced Microcirculation
Vasodilation is brought about by cold laser therapy, which also widens blood vessels and enhances microcirculation. This increased blood flow is essential for the delivery of nutrients, immune cells, and oxygen to the targeted tissues. It also aids in the clearance of waste products from metabolism and promotes the healing process.
Neurotransmitter Modulation
The possibility of using cold laser treatment to alter neurotransmitter levels has been investigated recently. Both the inflammatory response and the feeling of pain are influenced by neurotransmitters. The analgesic effects seen in a variety of clinical applications may be attributed to cold laser therapy’s influence on neurotransmitter activation.
Conclusion
One example of how science and medicine are advancing together is cold laser therapy. Its basis in photobiomodulation, and cellular process modulation has driven it into a therapeutic domain spanning multiple medical specialties. The potential of cold laser treatment as a valuable tool in encouraging cellular healing is highlighted by its diverse effects, which include the reduction of inflammation and oxidative stress, as well as the increase of cellular repair and immunomodulation.